What is Accessibility?
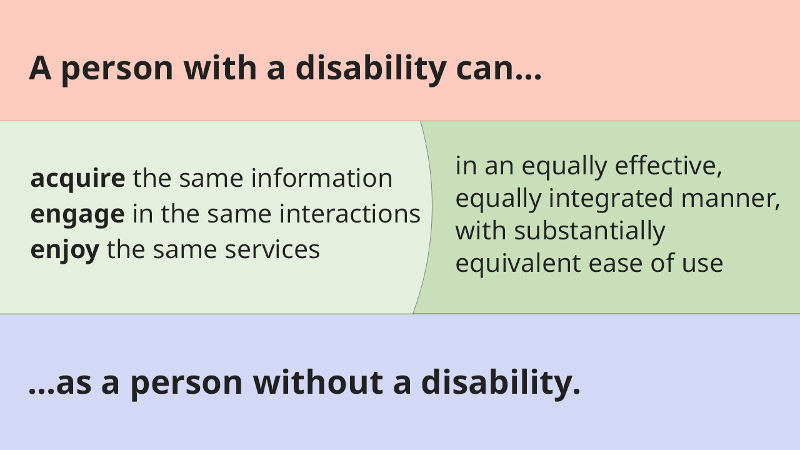
Accessibility is shaped by what we need to do, our interactions with the environment, and our personal preferences. Educational materials and technologies are “accessible” to people with disabilities if they are able to “acquire the same information, engage in the same interactions, and enjoy the same services” as people who do not have disabilities. As a person with a disability, you must be able to achieve these three goals “in an equally integrated and equally effective manner, with substantially equivalent ease of use” (Joint Letter US Department of Justice and US Department of Education, June 29, 2010).
Accessibility is a simple concept in theory, but it can be complicated in practice. What is accessible to someone with a visual disability is not necessarily accessible to someone with a learning disability.
At the AEM Center, we take the approach of asking some additional questions beyond, "Is it accessible?"
- To whom is it accessible?
- Under what conditions?
- For which tasks?
This recognizes that accessibility is shaped by what we need to do, our interactions with the environment, and our personal preferences.
To learn more about accessibility in the digital space view An Introduction to Digital Accessibility from The Office for Civil Rights.
Explore all the videos in our Accessible Learning Across the Lifespan series.
Accessible educational materials (AEM) are print- and technology-based educational materials, including printed and electronic textbooks and related core materials that are designed or enhanced in a way that makes them usable across the widest range of learner variability, regardless of format (e.g., print, digital, graphic, audio, video).
Accessible formats provide the same information in another form to address the barriers text-based materials can present for some learners. Examples of accessible formats include audio, braille, large print, tactile graphics, and digital text conforming with accessibility standards. See Accessible Formats.
Accessible technologies are the hardware devices and software that provide learners with access to the content in accessible digital materials. These technologies are designed to be flexible and provide supports that benefit everyone - they are universally designed.
Assistive technologies are designed to address specific barriers learners with disabilities may face when they interact with their materials. Examples of assistive technology include text-to-speech, screen readers and speech recognition. Assistive technology services assist learners with disabilities in selecting, acquiring and using the assistive technologies that are the best match for them.
In practice, the line between what is accessible and assistive technology can become blurred, especially as more assistive technology is included as built-in accessibility features on the consumer devices many learners and families already own.
To further explore concise definitions and explanations of common terms and acronyms related to AEM and its features, visit the AEM Glossary.
Visit the video titled An Introduction to Digital Accessibility for People with Disabilities from the Office for Civil Rights to learn more about accessibility in the digital space.
